In the world of music theory, chord progressions play an integral role and are often considered the backbone of a song.
These chord sequences, whether intricate or simple, convey emotions and moods that words might not adequately express.
From well-established musicians to fledgling novices, the understanding and application of classic chord progressions can refine one’s musicianship and elevate one’s compositions.
Despite the influx of technological aids, mastering these progressions remains a crucial part of musical study.
These staples of songwriting are not just influential within the sphere of classical music, but permeate all genres.
They serve as a testament to the universal language that is music.
Table of Contents
Classical Chord Progressions
I-V-vi-iii-IV-I-IV-V (1-5-6-3-4-1-4-5)
A rich tapestry that oscillates between stability and tension, brightness and contemplation.
Is a nuanced and expressive sequence, commonly found across diverse musical styles, marked by its elegant balance of major and minor chords, offering a complex yet cohesive pathway for conveying a broad spectrum of emotional tones.
- Difficulty: Easy
- Example: D – A – Bm – F#m – G – D – G – A (Key of D major)
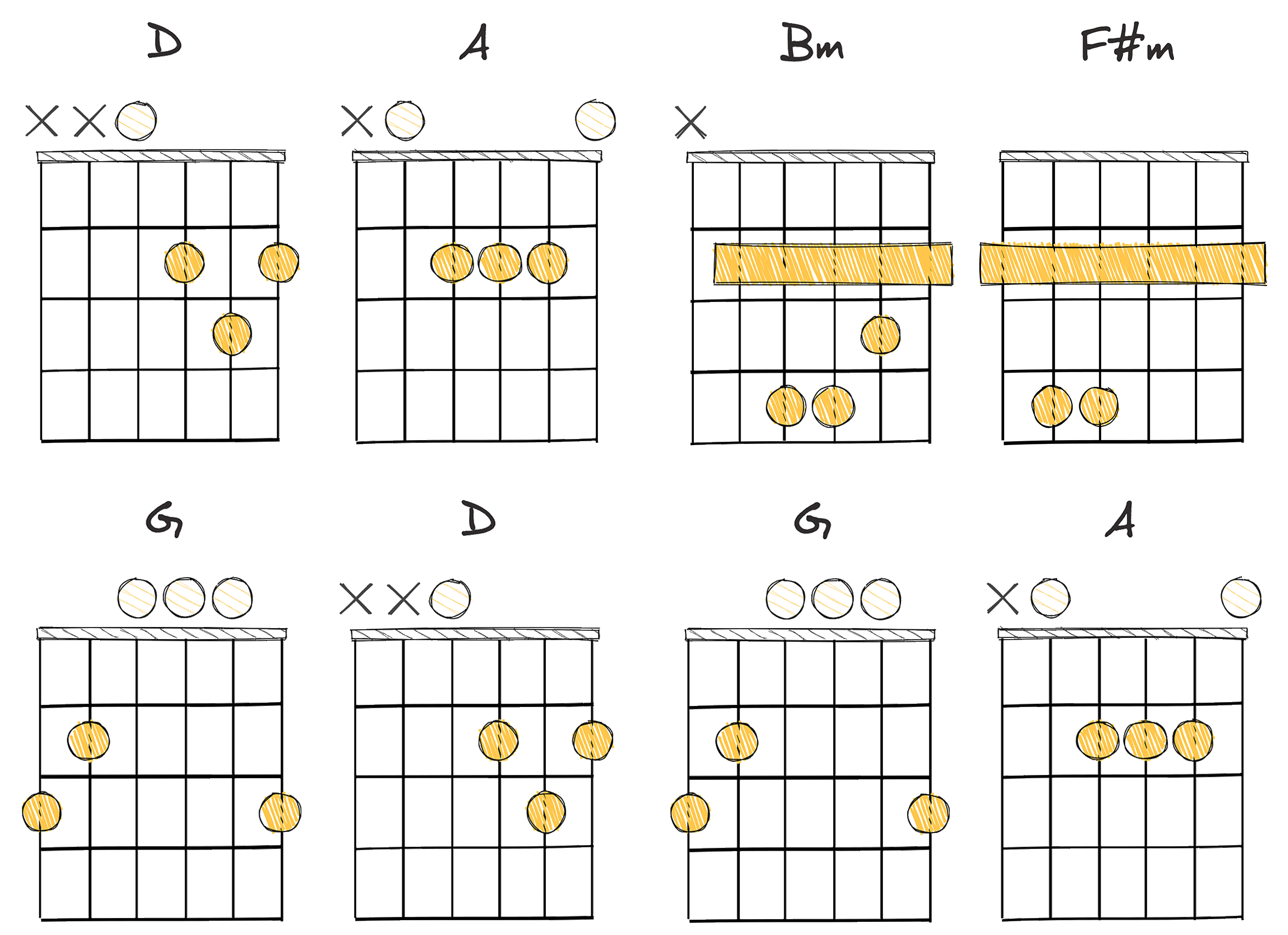
By exploring the chord progression of I-V-vi-iii-IV-I-IV-V (1-5-6-3-4-1-4-5), which unfolds in the key of D – A – Bm – F#m – G – D – G – A, we uncover foundational components that can be widely found across various musical styles.
The progression begins with the D chord, the tonic chord in the key of D major.
The tonic chord’s primary role in a musical piece is to establish a sense of home and stability, setting the stage for the ensuing harmonic journey.
Next, the progression shifts to the A major, dominant chord in this key.
Dominant chords create tension that yearns for resolution, injecting energy and anticipation into the music.
In many cases, they are the driving force that propels the melody forward, and this inherent tension is a hallmark of many musical genres.
Following this, the progression moves to B minor, a minor chord built on the sixth degree of the D major scale.
This minor chord adds a touch of wistfulness or contemplation to the music, contrasting the brightness of the major chords and allowing for greater emotional depth.
Transitioning to the F# minor, a minor chord on the third degree further enriches the melancholy tone.
This shift provides a reflective color contrasting with the bright and buoyant major chords.
Next, the progression introduces the G major chord, a subdominant chord in this key.
Subdominant chords bridge the tonic and dominant, often leading the listener back to the familiar home base or to further harmonic explorations, creating a full and satisfying musical narrative.
The sequence then returns to the tonic D major, reaffirming the central key before engaging the subdominant G and the dominant A again.
This cyclical return weaves the chords into a coherent and resonant whole.
The I-V-vi-iii-IV-I-IV-V progression (D – A – Bm – F#m – G – D – G – A) illustrates a harmonious blend of major and minor chords, creating a rich tapestry of emotions that can be both uplifting and poignant.
Whether in pop ballads, rock anthems, or even jazz standards, understanding this progression’s inner workings offers musicians the tools to craft compelling and versatile compositions.
By dissecting the structure, the tension and release mechanisms, and the alternating minor and major tones, we glimpse the beauty and complexity at the heart of music.
This progression is a perfect example of how melody, harmony, and rhythm converge to convey a wide emotional spectrum, painting a vibrant musical landscape that resonates with listeners across the globe.
I-V-vi-IV (1-5-6-4)
A versatile, emotional chord progression, pivotal in countless hits.
The I-V-vi-IV chord progression is a popular and timeless sequence of chords used extensively in various musical genres, particularly pop and rock. It is characterized by its shift of a major key to its relative minor, creating an emotive musical effect that is both uplifting and melancholic.
- Difficulty: Easy
- Example: C – G – Am – F (Key of C major)
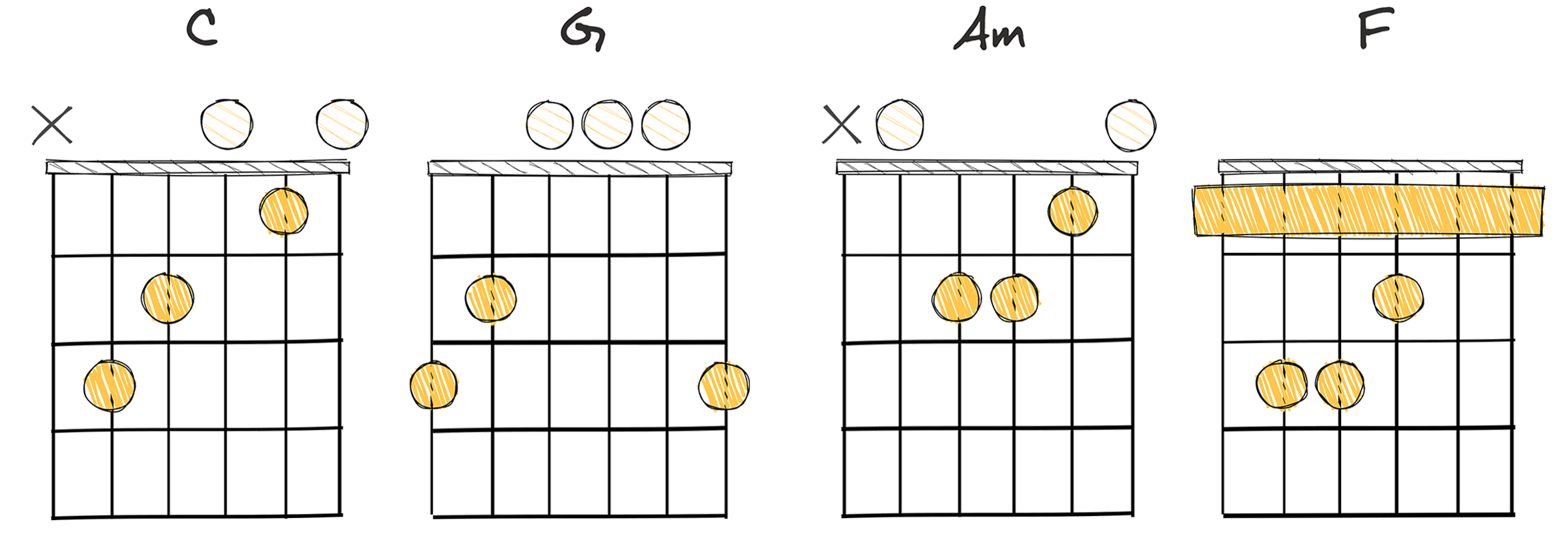
In the vast landscape of music, one of the most essential and foundational chord progressions musicians frequently come across is the I-V-vi-IV progression, or in the key of C major: C – G – Am – F.
Historically, this progression found its roots in the classical ages and has since permeated into several other genres.
To understand its popularity and significance, it’s crucial to appreciate the smooth and melodic nature this progression provides to any composition.
The simple structure of the I-V-vi-IV progression offers an exceptional level of versatility, allowing musicians to craft diverse moods and narratives within their music.
The beauty of the I-V-vi-IV progression lies in its structural simplicity that provides an excellent stepping stone for novice musicians.
Its ease of play does not just aid learning, but also serves as a fundamental backdrop for songwriters and composers to build harmonic complexity.
The I-V-vi-IV progression is not limited to the composition of melodies; it also provides ample room for improvisation.
Over time, musicians have experimented with it, adding their own unique touches and color, thus contributing to the dynamic nature of this chord progression.
Despite its simplicity and ease, the I-V-vi-IV progression has been at the helm of numerous musical masterpieces.
Whether it’s the soothing lullaby of a pop ballad or the powerful backbone of an energetic rock anthem, this progression has shown its diverse applicability.
Given the rich history, enduring popularity, and the creative possibilities of the I-V-vi-IV progression, it’s no wonder it forms an indispensable part of a musician’s toolkit.
In emphasizing the importance of this progression, we identify with the sentiment that its mastery is paramount for any serious musician and composer.
ii-V-I (2-5-1)
The ii-V-I progression: The cornerstone of harmonic movement in music.
The ii-V-I progression is a common chord sequence used widely in many genres of music, particularly classical music. It’s an indispensable tool for musicians as it forms the harmonic foundation of many songs and is often used as the underlying structure for melodies and improvisation.
- Difficulty: Intermediate
- Example: Dm – G – C (Key of C major)
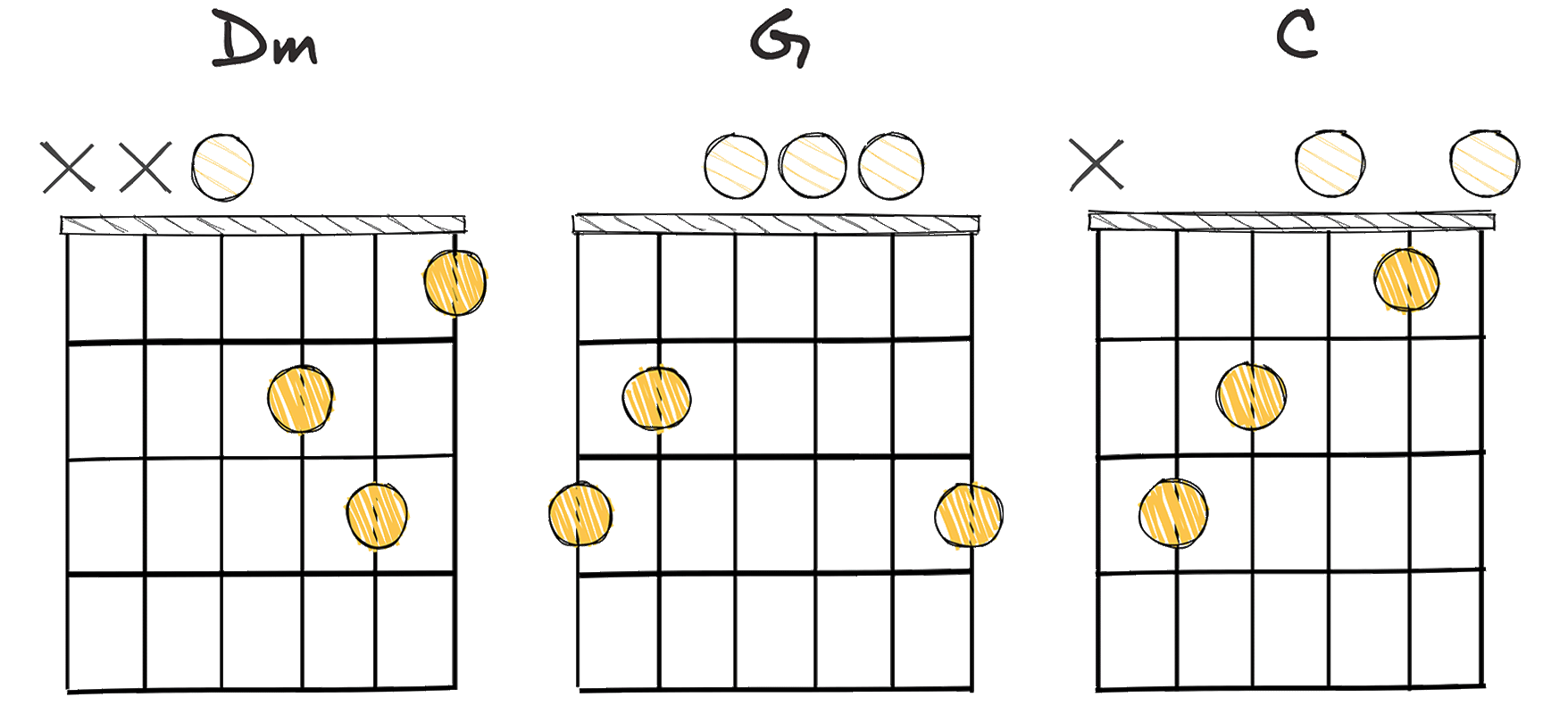
One of the most recognized and essential chord progressions in music is the ii-V-I (2-5-1) progression.
This progression is predominantly found in jazz music, but its influence extends into various other genres as well.
The technique of the ii-V-I progression was adopted over centuries, forming an inherent part of classical music structure.
Considered to be at an intermediate level to play, its applicability and versatility make it a beneficial addition to any musician’s toolbox.
Quite remarkable in the realm of harmonies and melodies, the ii-V-I (2-5-1) progression in C Major would be Dm – G – C.
The intermediate yet profound framework involves a minor, a major, and a dominant chord, resulting in a tension and resolve dynamic that lies at the heartbeat of music.
The intimate interaction between these chords forms a captivating harmonic structure with a perfect cadence at the end.
This progression’s unique characteristic is a resolve mechanism that attracts the listener’s ear, making it an absolute favorite among composers and music arrangers.
The ii-V-I progression can surprisingly be ingrained in a multitude of song structures, modifying its tonal landscape to fit the song’s emotion.
Whether it’s in composed solos or jam sessions, this chord progression has a permanent stamp in the music industry.
Often, this progression may sound different based on the performance, but the structure remains consistent, attributing to its universal appeal.
Understanding the ii-V-I progression enriches your ability as a composer, as it opens up a world of possibilities for melodic and harmonic exploration.
Practice certainly plays an integral part in mastering this chord progression, and in time, its applicability becomes instinctual.
Despite its crucial role, the ii-V-I progression is just one fragment of the vast world of music theory that holds its place in the evolution of music.”
In the journey of understanding classical chord progressions, the ii-V-I progression will always be a steadfast anchor, regardless of the genre or era of music.
vi-IV-I-V (6-4-1-5)
A timeless progression, offering a familiar yet emotive musical journey.
The vi-IV-I-V progression, also known as 6-4-1-5, is a pivotal music sequence particularly popular in classical music that creates a strong tonal variety, pushing the melody forward. This progression, often used in many well-known compositions, allows musicians to create a harmonious balance and a sense of resolution in their pieces, marking it vital for any aspiring musician to learn.
- Difficulty: Easy
- Example: Am – F – C – G (Key of C major)
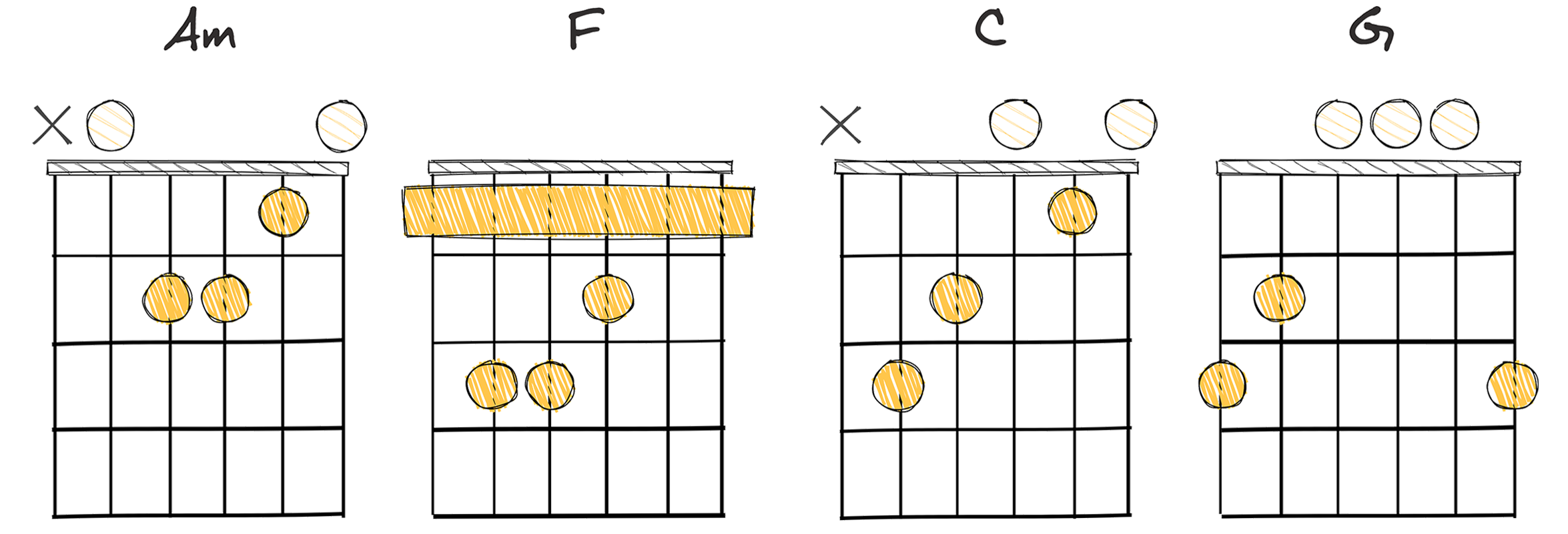
When we dive into the world of classical chord progressions, it’s important not to overlook the vi-IV-I-V (6-4-1-5) progression.
Known for its melodious tune and easy playability, it happens to be one of the greatest gems of music theory.
This particular progression, forming an integral part of both classical and contemporary music, has a deep-rooted history in music composition.
It dates back to the period of the Baroque and Classical eras, making an indelible mark on the compositions of the times.
The vi-IV-I-V progression was a pivotal turning point in shaping the course of musical expression, challenging the repeated dominance of other classic progressions.
Supporting this statement, musicologists believe that this chord progression instigated a sort of ‘musical revolution.’ They believe it challenged dominant music structures, piloting a novel wave of creativity among composers and musicians alike.
Furthermore, it has been used aplenty in the compositions of renowned musicians, thereby bolstering its status in the music world.
Assuming the key of C major, the chords in this progression would be Am – F – C – G.
Contrasting the individual sounds of these chords can make for an elegant and pleasing progression, suitable for a variety of musical genres.
Enduring to our days, the progression has gone on to conquer the world of pop music.
It has maintained its relevance and usability even in the modern, fast-evolving music scenario.
Ultimately, learning classical chord progressions such as vi-IV-I-V can certainly enhance one’s understanding of music theory.
Whether you’re a beginner starting out on your musical journey or an experienced musician seeking inspiration for your next composition, this chord progression stands as a must-know.
Mastering this progression can act as a touchstone for your musical journey, expanding your musical lexicon and enabling you to create enchanting melodies.
I-IV-ii-V (1-4-2-5)
A timeless progression, foundational to understanding classical composition.
The I-IV-ii-V (1-4-2-5) progression is a staple in classical music, tracing its origins back to the Baroque period. This harmonic pattern provides a strong sense of resolution and is often used for verses or choruses in various genres, making it a central piece in a musician’s toolkit.
- Difficulty: Easy
- Example: C – F – Dm – G (Key of C major)
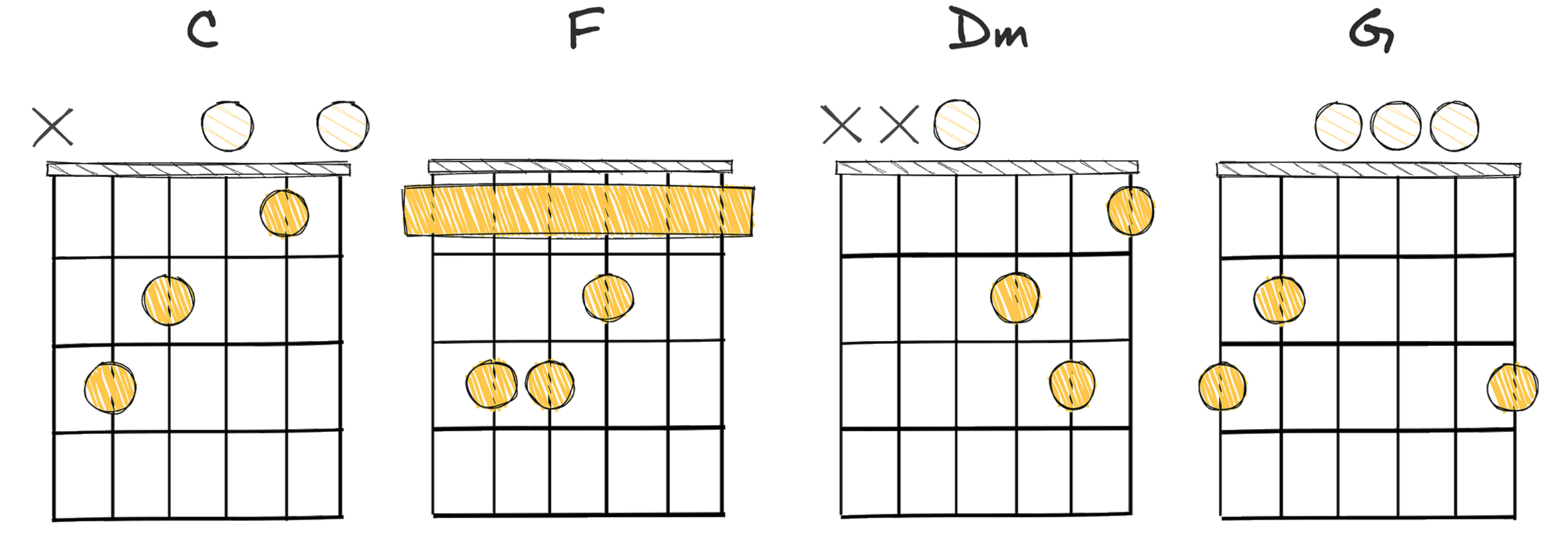
The I-IV-ii-V chord progression is a significant aspect of classical music theory.
It is often present in various music genres, and despite its formal structure, it lends itself to a wide range of creative reinterpretations.
Such is the charm of this chord progression, that it has been ubiquitous in Western music for several centuries.
This can be further attributed to its capability of facilitating smooth harmonic flow while still producing a resonating thematic melody.
The I-IV-ii-V chord progression can be implemented in an effortless way, thereby making it accessible to musicians at all levels.
Beginners could start by playing C – F – Dm – G, while professionals could further experiment with different notes and timings.”
This classical chord progression has been effectively used in countless songs to generate a musically gratifying experience.
At the heart of this chord progression’s widespread usage lies its versatile nature.
It easily accommodates a variety of musical genres, from pop and rock to jazz and blues, thereby serving as a popular choice among musicians and composers.
An interesting aspect of the I-IV-ii-V progression is its slight deviation from the more commonly used I-IV-V progression.
The inclusion of the ii chord introduces a touch of minor tonality to the sound, thereby creating a subtly nuanced sonic effect.
The I-IV-ii-V chord progression’s inclusion in modern music education further elucidates its impact and significance.
It is often taught as a fundamental aspect of music theory, as understanding and mastering it can open up a world of creative opportunities for budding musicians.
This chord progression can also serve as a stepping stone to comprehend more complex harmonic structures, thus allowing for continued musical growth and exploration.
Understanding and employing the I-IV-ii-V chord progression indeed signifies greater musical fluency and creativity – a milestone that every earnest musician should aspire to reach.
While these chord progressions serve as structural blueprints, it is up to the individual musicians to impart their unique flavor, thereby bringing to life the magic that continues to make music an enduring means of human expression and connection.
I-vi-ii-V (1-6-2-5)
A harmony staple, creating a smooth, compelling circular motion.
The I-vi-ii-V chord progression, often referred to as the ‘turnaround’ progression, is a classic pattern found in many genres, including jazz and pop music. It represents a series of transitions from the home chord (I) to others that create tension, and then provides a satisfying resolution back to the beginning, which makes it ideal for introducing movement and dynamics into songs.
- Difficulty: Intermediate
- Example: C – Am – Dm – G (Key of C major)
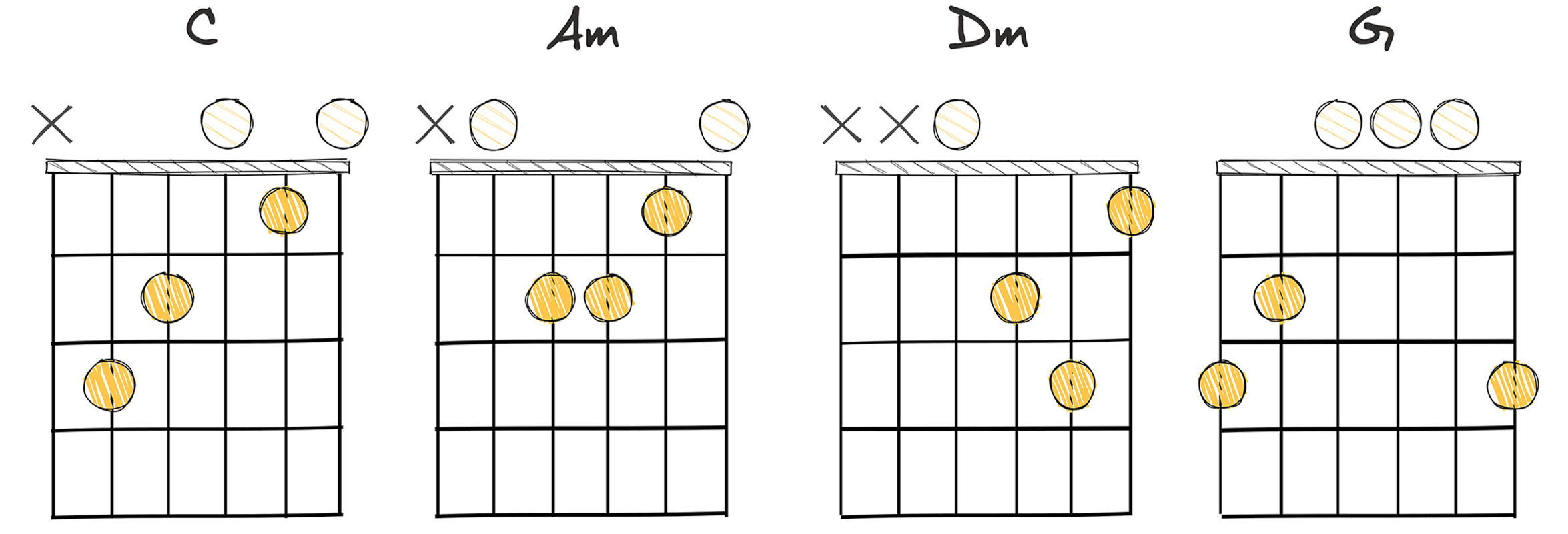
The I-vi-ii-V (1-6-2-5) chord progression, commonly known in the music world as the ‘turnaround’ progression, is a sequence of chords that is intermediate to play and provides a compelling sense of forward momentum and resolution in a song.
This progression is heavily influential in pop, jazz and rock music, playing a crucial part in shaping the harmonic structure of numerous songs and thereby possessing unparalleled importance for any aspiring musician.
A deep understanding of this progression can provide the musician with an array of possibilities in creating aesthetically pleasing and melodically intriguing music.
Historically, the I-vi-ii-V progression has been a cornerstone in the formation and development of many music genres, and this trend seems to be continuing well into the present day music industry.
It serves as a recurring progression across the works of countless famous musicians and bands, further underscoring the importance of studying and mastering the I-vi-ii-V sequence.
The immense popularity of the I-vi-ii-V chord progression is not without reason.
Apart from providing a strong harmonic foundation, it also offers an easy framework for improvisation, thus being a useful tool for musicians of varying proficiency levels.
An in-depth understanding of the theory behind the I-vi-ii-V progression can help musicians explore different musical styles and expand their creative boundaries.
When adopted and used adeptly, it can completely transform a piece of music.
It provides an intriguing backdrop for melodies, thus shaping the overall musical narrative of a composition.
Therefore, the I-vi-ii-V progression is an indispensable tool in the toolkit of any dedicated musician, irrespective of their preferred genre.
In conclusion, the ubiquitous I-vi-ii-V progression can be a source of inspiration and advancement in the hands of a proficient and creative musician.
Its importance in the sphere of music composing and improvising should not be underestimated, which is why every musician should seek to understand and integrate it into their practice and performances.
Armed with the knowledge of this progression, musicians will have at their disposal a powerful tool to take their music to the next level.
I-iii-IV-I (1-3-4-1)
A timeless sequence, resonating with elegance and introspective emotion, bridging classical and contemporary expressions.
A richly evocative chord progression, the I-iii-IV-I sequence offers a blend of familiarity and novelty. Its gentle harmonic tension lends itself to both reflective and emotional pieces, providing a pathway for composers to explore delicate interplay between melody and harmony. Its adaptability across various musical contexts underlines its timeless grace and subtle charm.
- Difficulty: Intermediate
- Example: C – Em – F – C (Key of C major)
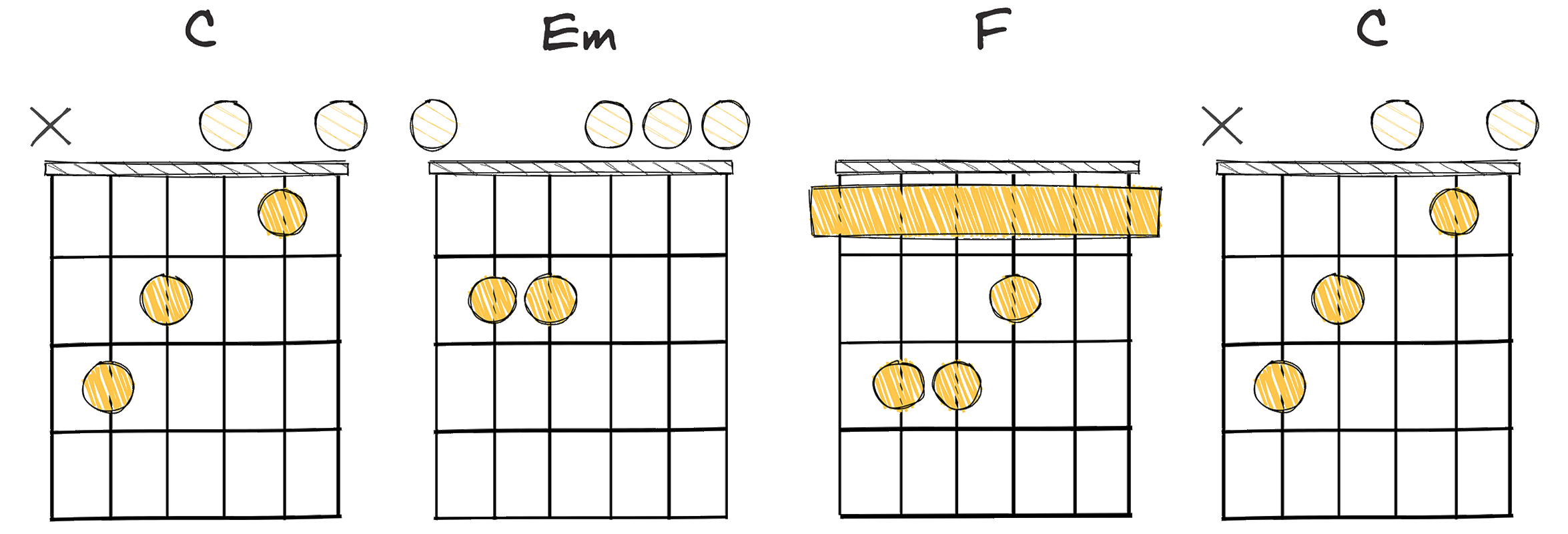
The I-iii-IV-I chord progression is an elegant sequence that resonates with the music’s delicate and expressive nature.
This progression finds its niche as a thoughtful and evocative pattern imbued with a gentle melodic tension within the rich tapestry of musical traditions.
Hailing from the classical musical canon, the I-iii-IV-I progression has been a component in pieces that evoke a more reflective and emotional response, distinguishing itself from other more prominent progressions.
Though not as widely recognized as some other progressions, it has a subtle charm that captures the imagination of composers and listeners alike.
Its harmonic structure is such that it allows for exploration and expression, lending itself to both classical compositions and more contemporary pieces, thereby showcasing its adaptable nature across musical eras.
In essence, the I-iii-IV-I progression is approachable and complex, offering a blend of familiarity and novelty that can be tailored to various musical contexts.
Its structure encourages musicians to delve deeper into harmonic relationships, opening doors to nuanced creativity.
For instance, the I-iii-IV-I progression in the Key of C major translates to the chords C – Em – F – C.
What sets this progression apart is its ability to evoke a sense of longing or resolution, depending on how it’s employed within a composition.
Despite not being as omnipresent as some other progressions, it has a timeless quality that offers many emotional expressions.
Through thoughtful arrangement, rhythmic variation, and mindful orchestration, musicians can utilize this progression to craft pieces that resonate with depth and originality.
Indeed, embracing this understated chord progression empowers a musician to explore the delicate interplay between harmony and melody, enhancing technical prowess and artistic sensitivity.
Its integration across different genres reinforces its value in fostering a comprehensive musical understanding, allowing for a more profound connection with the listener.
Lastly, the timeless grace of the I-iii-IV-I progression solidifies its place in the musical lexicon.
Though perhaps more subtle in its appeal, it is a chord progression that offers endless possibilities for innovation and expression.
As such, it is a valuable addition to the repertoire of any musician seeking to deepen their craft and engage with music on a more personal and thoughtful level.
vi-ii-V-I (6-2-5-1)
A harmonically satisfying staple in countless jazz and pop compositions.
The vi-ii-V-I progression, also known as the 6-2-5-1, is a classic series of chords often used in various music genres for its pleasing resolution from tension to release. It’s characterized by a minor tonal beginning that resolves to a major tonality, creating a compelling harmony that is foundational in learning musical composition.
- Difficulty: Easy
- Example: Am – Dm – G – C (Key of C major)
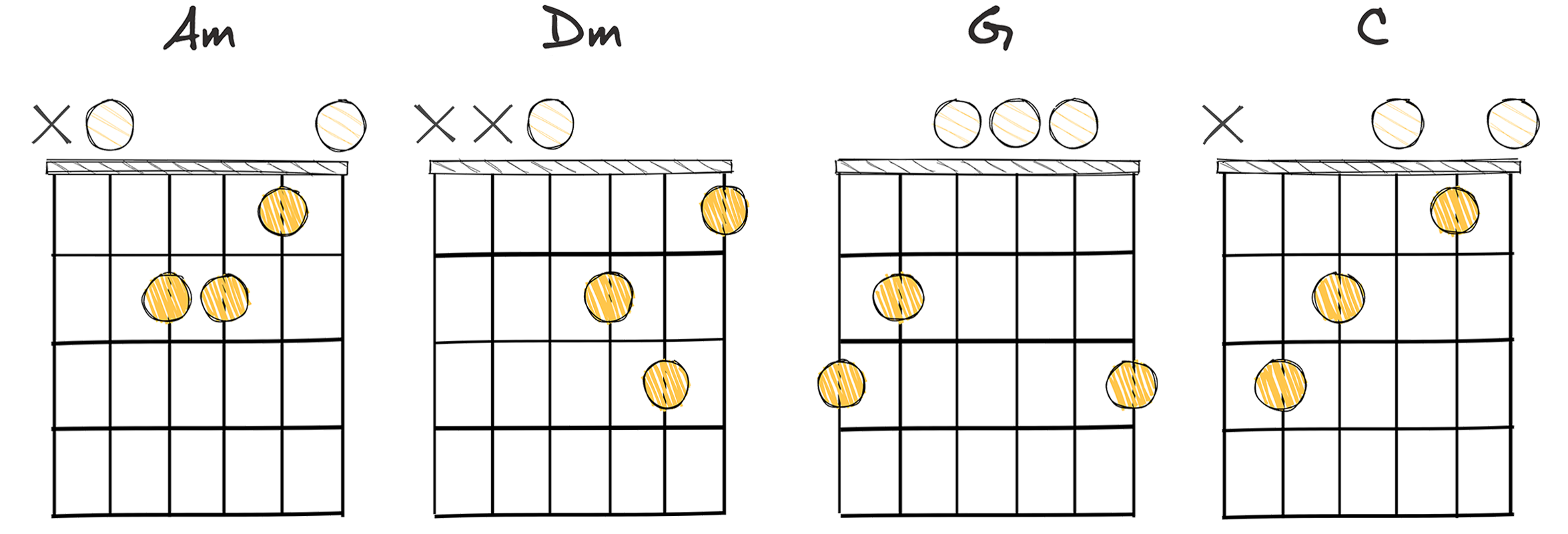
The chord progression vi-ii-V-I, often referenced in numerical format as 6-2-5-1, is one of the most fundamental chord progressions in both classical and popular music.
Its impressive ubiquity and versatility have solidified its standing as one of the most foundational sequences in music theory.
History reveals the roots of the vi-ii-V-I progression in the essence of Baroque, Romantic, and Classical era compositions, marking it an essential learning point for aspiring musicians.
Supporting the previous statement, the 6-2-5-1 progression was central to the development of musical movements across centuries and is often found in pieces that shaped the course of music history.
In terms of playability, the vi-ii-V-I progression is remarkably straightforward and allows for an easy transition between chords, making it a fertile ground for beginners to practice and learn chord movements.
When specifically looking at the Key of C major, the vi-ii-V-I progression translates to the chords A minor – D minor – G major – C major, which are easily playable and transferable in various musical arrangements.
What makes this progression widely favoured by composers is its ability to naturally cycle back to the starting chord, ensuring a smooth harmonic journey.
This smooth journey is exactly what keeps the vi-ii-V-I progression relevant and in use to this day, as it provides a solid base for innovative explorations.
It’s safe to say that understanding and mastering the 6-2-5-1 chord progression is a crucial step in a musician’s journey, whether they aspire to make music in a classical or modern style.
Therefore, musicians of every level should strive to learn the vi-ii-V-I progression and explore its potential in their musical creativity and expression.
Given its rich history and the simplicity in its playability, the vi-ii-V-I chord progression is an invaluable musical tool that every musician must familiarize themselves with, irrespective of their style or genre preference.
I-iii-IV-V (1-3-4-5)
A foundational progression, shaping tension and resolution in classical music.
The I-iii-IV-V chord progression is a common sequence found in classical music, offering a perfect balance of tension and release. It starts on the tonic, or home chord, moves to the mediant, then the subdominant and finally to the dominant, which pulls strongly back to the tonic, thereby creating an appealingly straightforward and predictable harmonic route.
- Difficulty: Easy
- Example: G – Bm – C – D (Key of G major)
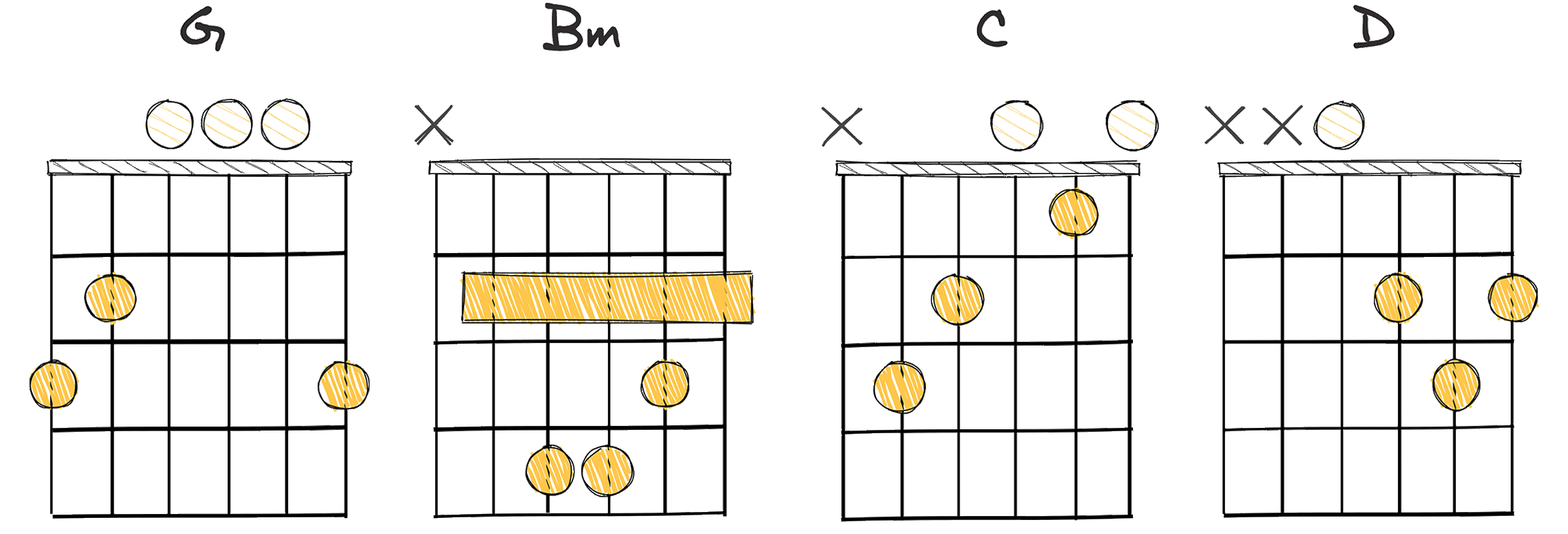
One of the valuable classical chord progressions that every established or aspiring musician should learn is I-iii-IV-V, also represented by the numbers 1-3-4-5.
This vibrant progression is not just elegant and graceful; it is also relatively easy to play.
The stark beauty of this progression has its roots deeply embedded in classical music, and it’s often used to evoke a sense of nostalgia and classicism.
This progression is highly versatile, and it’s commonly encountered across a range of musical genres, including pop, rock, gospel, and of course, in the realm of classical music.
The sequence I-iii-IV-V showcases a remarkable harmonic richness.
It’s characterized by interesting tonal shifts, which add depth and thick texture to a musical piece.
It is important to note that while this progression is relatively easy to play, its effectiveness lies in understanding how the chords work together to create a striking resonance.
A keen understanding of this progression allows musicians to exploit its full harmonic potential to create emotionally diverse soundscapes.
When exploring this progression, remember that letting the chords play out in interesting rhythmic patterns can result in highly compelling musical arrangements.
It’s an undeniably beautiful progression that has been affectionately adopted by many musicians.
It’s a must-know asset for musicians looking to infuse their music with a touch of classical elegance.
This progression is an exceptional journey through tonal shifts that offer an alluring sonic experience.
It is an essential part of a musician’s creative toolbox.
The I-iii-IV-V progression, in all its melodic richness and harmonic diversity, holds a vital place in music history.
It will continue to be a favorite choice for musicians in the creation of enthralling and memorable pieces of music.
Learning and mastering this progression is a great step towards achieving a high level of artistic prowess.
Its simplicity, coupled with the depth of character it adds to music, makes it an indispensable progression for every musician.
IV-V-I (4-5-1)
The “IV-V-I” is a timeless progression, the backbone of classical music.
The IV-V-I progression is a well-known and frequently used sequence in both classical and popular music, often signaling the end of a musical phrase or piece. It is characterized by its sense of resolution, as the tension created in the ‘V’ chord is satisfyingly resolved when it moves to the ‘I’ chord.
- Difficulty: Easy
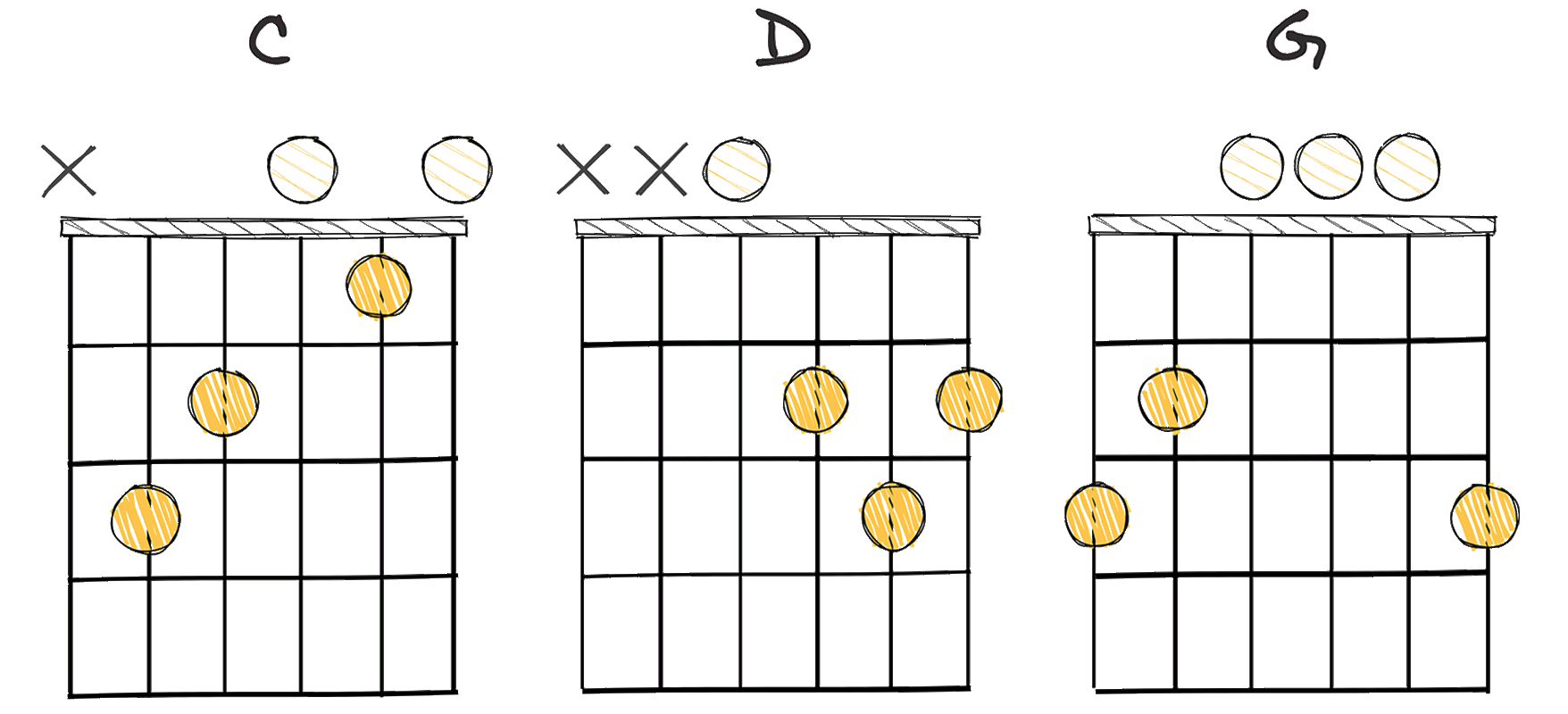
- Example: C – D – G (Key of G major)
In understanding the rich tapestry of music, one must appreciate the rhythmic precision and melodic nuances of classical chord progressions.
One such progression that resonates deeply with both novice and seasoned musicians is the IV-V-I (4-5-1) progression.
This enviable progression‘s history is not only riveting, but it also adds depth to the knowledge of any musician seeking to understand the progression in a historical context.
The IV-V-I chord progression, like many others, stemmed from classical-era compositions, where composers often relied on the progression to resolve pieces in a satisfying manner.
Cherished by music luminaries throughout the centuries, the IV-V-I progression has proven to be versatile for compositions across varying musical styles.
From the intricate baroque sonatas to the lively tunes of pop music, the IV-V-I progression has been a consistent and beloved player.
This progression’s timeless appeal is further highlighted by its use in modern compositions.
Novice musicians consider this progression easy to play because it requires only basic guitar fingering patterns, making it accessible to beginner-level musicians.
Regarding the chords in this progression, for a song in the key of G Major, the chords would be C – D – G, to represent the IV-V-I sequence.
Learning the IV-V-I progression thus equips a musician with a universal melodic tool, invaluable to the art of composition.
The sheer simplicity yet layered complexity of the IV-V-I progression in music makes it an enduringly valuable progression which every musician should strive to learn and understand.
ii-IV-V-I (2-4-5-1)
A foundational harmonic progression cultivating resolution and suspense in music.
The ii-IV-V-I chord progression, also known as the 2-4-5-1, is widely revered in the music world for its versatile and integral role in classical music compositions. It lays the foundation for a harmonious sequence with its distinctive sound, enabling musicians to generate a variety of melodies while maintaining a cohesive musical structure.
- Difficulty: Easy
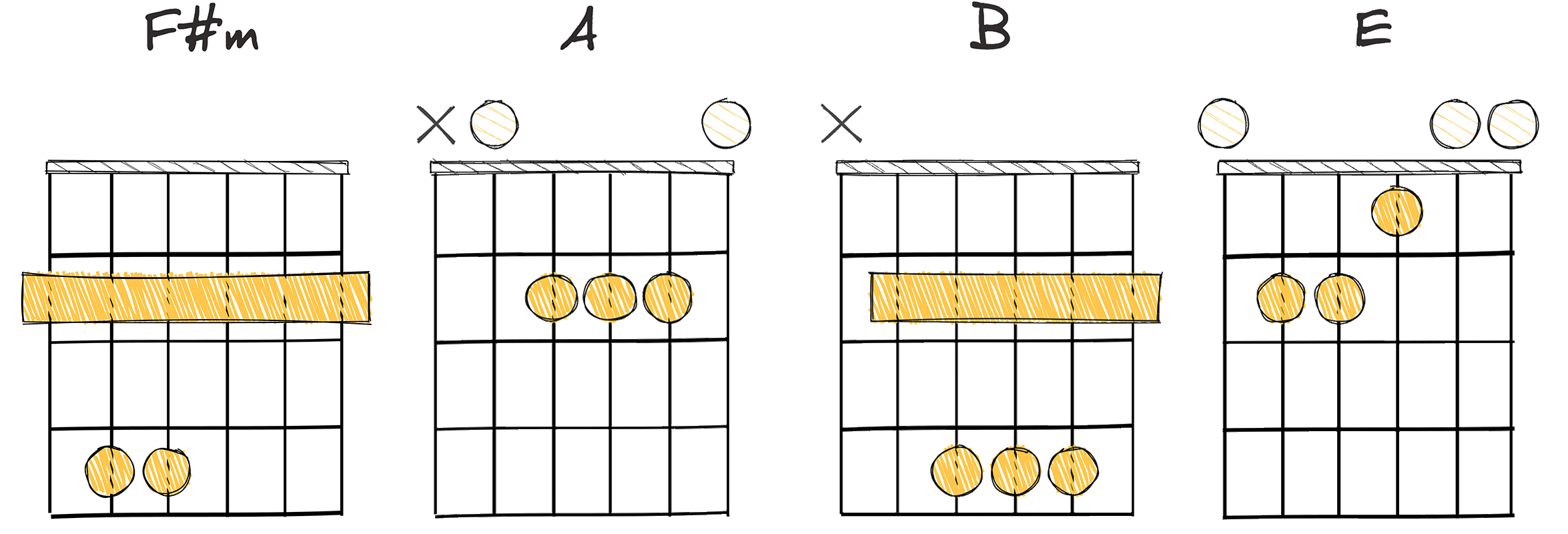
- Example: F#m – A – B – E (Key of E Major)
When exploring the rich tapestry of music history, it’s indisputable that certain chord progressions stand out due to their widespread usage and inherent melodic appeal.
One such chord progression is ii-IV-V-I (2-4-5-1).
While it might seem simple, this chord progression possesses a distinctively resonant sound that feels familiar yet layered.
Observant music lovers and practitioners will have come across this progression in numerous genres, attesting to its versatile and universal nature.
The roots of the ii-IV-V-I progression can be traced back to classical music, where composers and musicians discovered its potent potential to convey a wide range of emotions.
Over the centuries, this chord progression remained popular in many musical styles, evolving with the times while retaining its core melodic appeal.
This persistent popularity across styles and eras has made the ii-IV-V-I progression a fundamental part of musical composition.
The importance of understanding it cannot be understated for any aspiring musician.
One of the reasons why the ii-IV-V-I progression is essential for musicians to learn is because of its ease of play.
It’s a practical starting point for understanding music composition, especially for beginners learning to play an instrument or write a song.
The chords used in this progression, for the key of E Major, could be F#m, A, B, E.
This chord sequence generates a flowing rhythm and builds harmonic tension throughout a musical piece.
This tension typically resolves in satisfying fashion, providing listeners with an emotionally resonant experience.
In the expansive world of music, the ii-IV-V-I progression is one of many tools that musicians and composers employ to create compelling pieces.
However, its unique blend of simplicity and versatility make it a stepping stone that shouldn’t be overlooked.
As a musician, understanding the intricate workings of the ii-IV-V-I progression, its history, and its applications in various genres provides an invaluable foundation upon which much of your music education can be built.
Using and experimenting with the ii-IV-V-I progression will not only enhance your understanding of music theory but also expand your creative horizons as you explore the endless possibilities this progression presents.
I-V-IV-ii (1-5-4-2)
This progression offers a compelling resolution with its minor iv chord.
The I-V-IV-ii (1-5-4-2) is a classical chord progression that plays a crucial role in western music and is beloved for its emotional resonance. This progression offers a subtle and evocative combination of major and minor chords, making it perfect for a wide variety of musical styles and genres.
- Difficulty: Easy
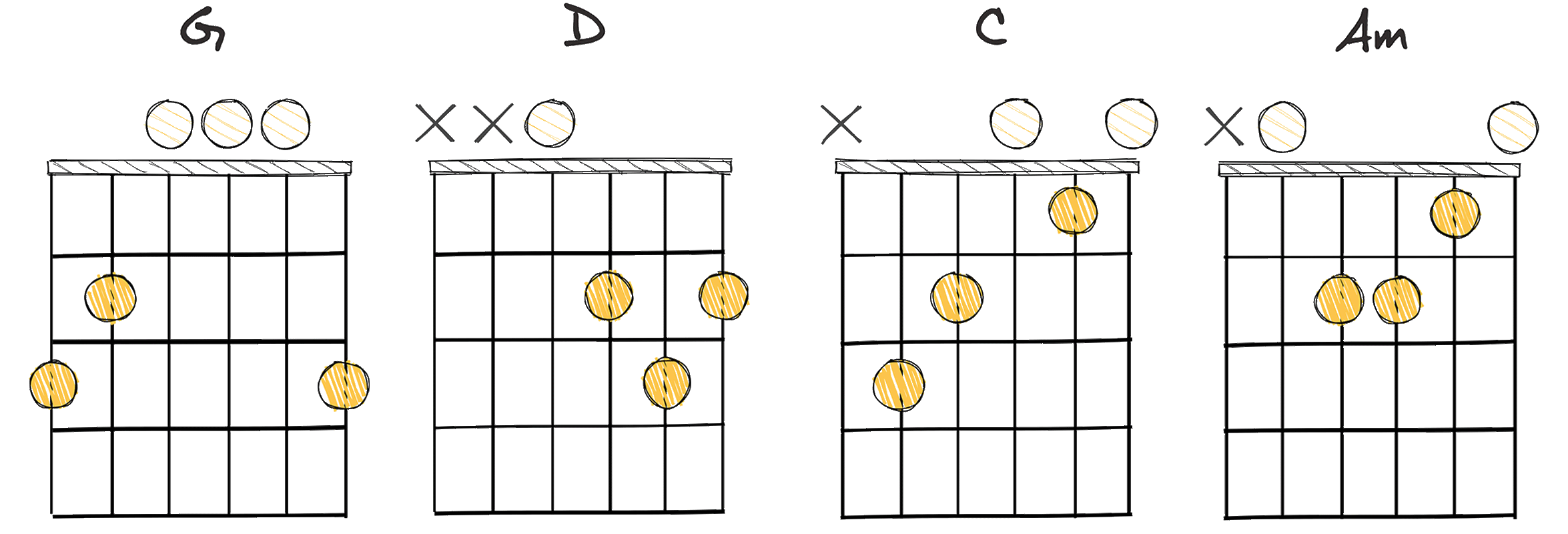
- Example: G – D – C – Am (Key of G major)
The I-V-IV-ii chord progression is one of the fundamental sequences in the realm of classic music.
It derives its significance from its historical roots, functionality, and the beautiful melodies it creates.
Over time, this progression has become a cornerstone in many musical compositions, spanning from classical compositions right through to modern-day pop songs.
Interestingly, this progression is rather easy to understand and to play, making it a popular choice for musicians of all levels.
With just the basic understanding of key signatures and chord relationships, you can easily grasp the use of this chord progression in your musical creations.
The main chords in the I-V-IV-ii progression in the key of G Major for example, would be G – D – C – Am, respectively.
Notably, picking up on the nuances of this progression and interpreting it in different ways can help musicians achieve a unique musical style.
It is through the understanding and application of such critical music theory concepts like the I-V-IV-ii progression that we can truly express the full bandwidth of human emotion within our musical narratives.
In the realm of music, such progressions provide a solid groundwork upon which we can build our melodies and harmonies.
As such, every aspiring musician should take the time to understand and learn these classical chord progressions.
They are the bridges through which we can connect notes, phrases, and ultimately express our creative vision.
Though subtle in its application, the impact of the I-V-IV-ii progression in music composition cannot be underestimated, as it has the capability to add depth and complexity to any melody.
I-V-ii-IV (1-5-2-4)
An iconic progression, merging resolution with tension for timeless melodies.
The I-V-ii-IV chord progression, commonly found in classical music, provides a harmonious arrangement that creates a balance between tension and resolution perfect for various composition styles. This sequence, consisting of the first (I), fifth (V), second (ii), and fourth (IV) chords of a key, serves as an essential foundation for musicians to understand chord structure and progression, enhancing their songwriting mastery.
- Difficulty: Easy
- Example: G – D – Am – C (Key of G major)
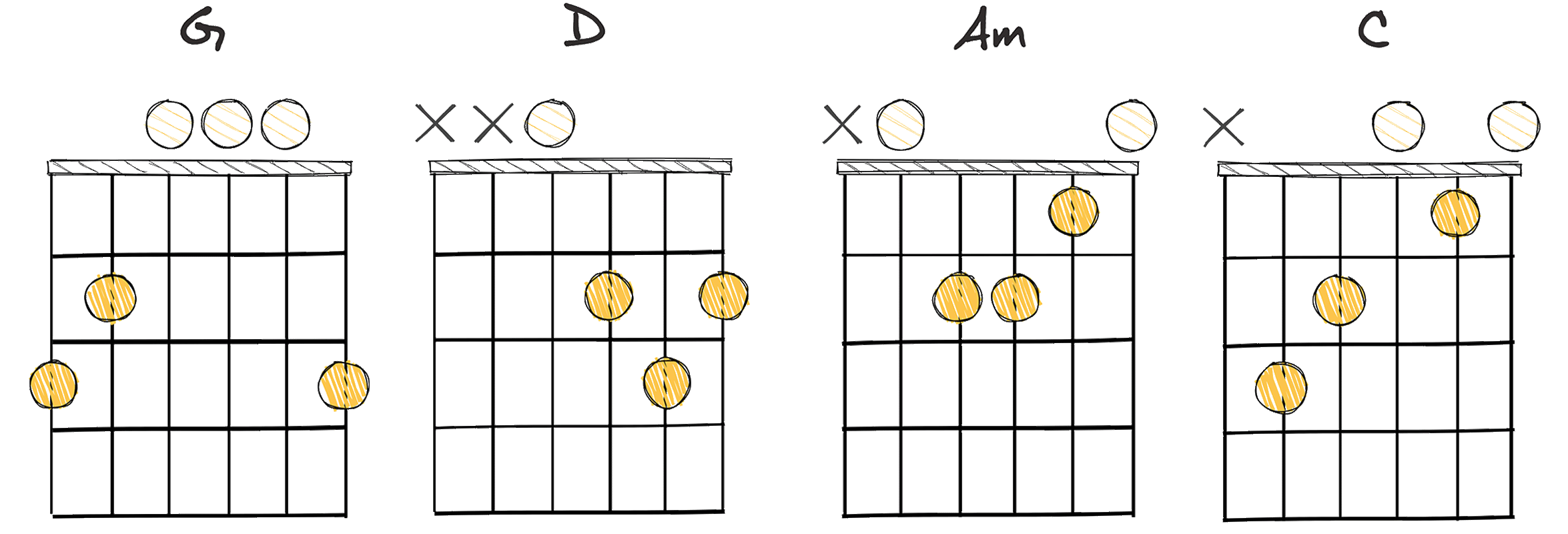
The chord progression I-V-ii-IV (1-5-2-4) is one of the most elementary and admired chord modulations in classical music, and it’s an absolute must to learn for musicians of all genres.
It stands out for its simplicity and versatility, making it easy for beginners to pick up and incorporate into their repertoire.
The Beatles, widely known for their timeless classics, used this chord progression in their hit song “Let It Be.”.
By using these four chords from the key of G major – G, D, Am, and C – they successfully created a song that is both enchanting and melodious, remarkable proof of this chord progression’s potential.
This chord progression I-V-ii-IV (1-5-2-4) became a staple in classical music and continues to be highly influential in modern music genres today.
Its widespread use throughout history is a testament to its melodic charm and harmonic balance.
Its prevalence reflects its ability to underpin multiple song structures, making it a key building block in the music composition process.
Careful integration of this progression in your compositions can result in harmonious and captivating music pieces.
The usefulness and accessibility of this progression are perhaps why it’s an essential part of musical training and practice.
Understanding it helps musicians grasp fundamental concepts about music theory and chord relationships.
As an emerging musician, utilizing this simple but effective chord progression can open doors to further musical exploration.
It can prompt creative innovation and help musicians enhance their compositional skills.
Mastery of this progression could mean taking your music from good to truly exceptional.
Thus, it’s not just about playing these chords but about understanding their relative effect in a musical context.
While the chord sequence may seem basic, a deep understanding of its structure and functionality in a song can greatly elevate a musician’s proficiency.
vi-IV-I-V (6-4-1-5)
A popular, emotive progression used extensively in pop music.
The vi-IV-I-V chord progression is a classic sequence in music that is often used in pop, rock, and classical genres due to its compelling and satisfying resolution. This progression creates a natural sense of movement and growth in the music, starts with an emotional minor chord, moves to a stable major, resolves to the primary major key, and then finishes with an uplifting dominant chord to complete the cycle.
- Difficulty: Easy
- Example: Am – F – C – G (Key of C major)

Today, we are sailing through the musical seas to explore the vi-IV-I-V chord progression.
In its Roman numeral representation, this is pronounced as six-four-one-five and is commonly used in various music genres.
With origins deeply rooted in classical music, this progression has a profound influence on modern music composition.
The musical journey of this pattern of chords can be followed throughout the centuries, demonstrating its versatility and timeless allure.
The simplicity and ease of playing vi-IV-I-V is a benefit that is highly cherished by beginners.
This chord progression facilitates a smooth transition between the chords, making it an absolute delight for musicians who are just starting their journey.
This progression can be found in various genres and musical periods, further testifying to the versatility and adaptability of this pattern.
Also very useful in the process of composing new music.
Its rhythmic nature and soothing tonal characteristics create a comfortable foundation for melodies and lyrics.
Experimenting with different combinations within the vi-IV-I-V chord progression can also yield interesting variations.
Altering the duration of each chord, for example, can result in an entirely different feel and flow to the musical piece.
It is also worth noting that this chord progression is not just limited to the key of C major.
It can be transposed into any other key as desired.
This is an exciting feature for songwriters seeking to vary the mood or tone of their compositions.
In conclusion, the vi-IV-I-V chord progression is an essential tool in the toolkit of musicians across the globe.
Its simple, yet undeniably profound, structure produces evocative and memorable pieces of music.
I-vi-IV-V (1-6-4-5)
A timeless, universal chord progression foundational to many genres.
The I-vi-IV-V (1-6-4-5) chord progression is a crucial foundation in classical music, known for its melodic and harmonic balance. Serving as the backbone in many genres, from pop to blues, it often forms the cycle of chords in countless songs, creating a pleasing and catchy rhythm that is easily remembered by the listener.
- Difficulty: Easy
- Example: G – Em – C – D (Key of G major)
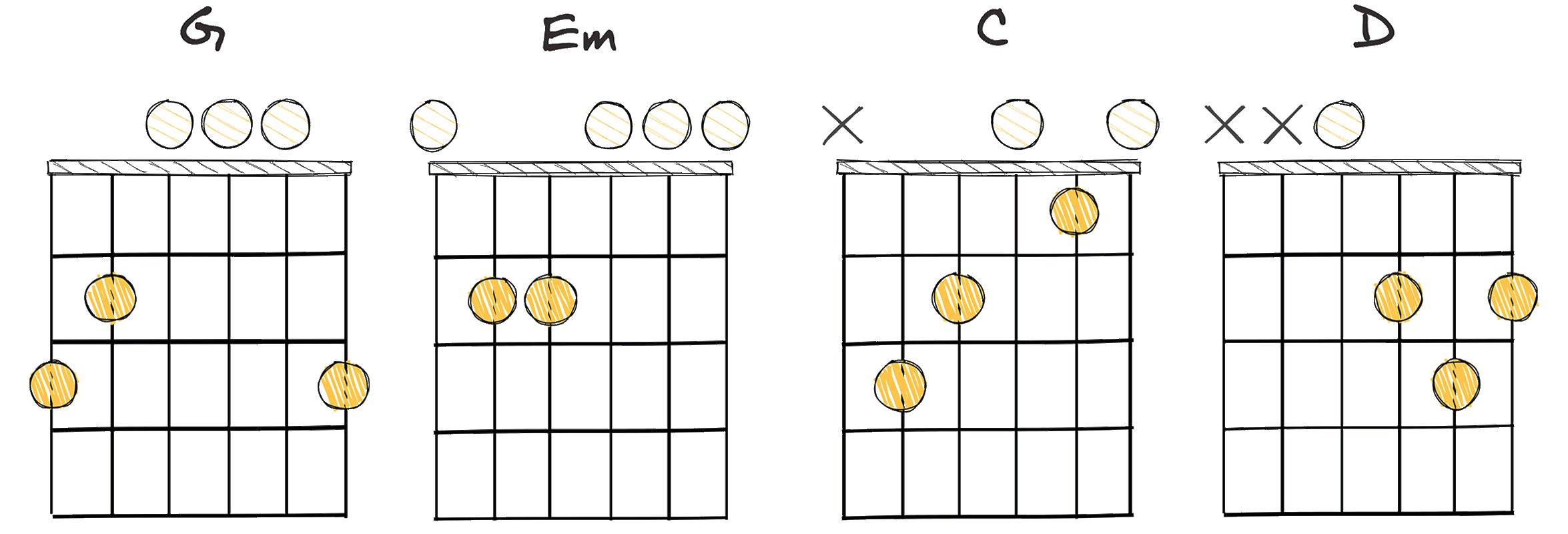
The I-vi-IV-V chord progression is a classic sequence that has its roots embedded deep in the history of music.
Among the various chord progressions, it holds a significant place for its recognizable and catchy qualities.
Originating from Western classical music, the I-vi-IV-V progression was later adapted into folk, blues, and ultimately pop and rock music, thereby solidifying its universal appeal across genres and eras.
Thus, it is often branded as the ’50s progression, owing to its extensive usage in pop hits during this era, becoming practically a cliché within doo-wop music.
This statement highlights the profundity and versatility of the progression, where its application blurred the lines among diverse music genres.
Its simplicity and infectious quality helped in breaching the walls between classical and contemporary music.
In essence, the I-vi-IV-V progression is easy to play and can be transposed to different keys as per the requirements of a song.
Its relatively simple pattern allows musicians of all levels to experiment and create melodious musical pieces.
For a concrete example, in the Key of G major, the I-vi-IV-V progression would translate to the chords G – Em – C – D.
One of the most appealing qualities of the I-vi-IV-V progression is its resilience to becoming stale.
Despite its widespread usage, it continues to inspire and create fresh, memorable music.
Moreover, by altering the rhythm, dynamic range, or implementing chord substitutions, musicians have been successfully banking upon this progression to expanse the scope of their creative expression.
Consequently, mastering this fundamental chord progression truly paves the way for a musician to understand the interaction of harmony and melody in music.
Simultaneously, its applicability across a variety of genres endorses its significance in building a robust musical foundation and developing an all-rounded musical understanding.
Lastly, the enduring popularity of the I-vi-IV-V progression validates its Continued vitality in the fabric of music.
As such, it is certainly one of the classical chord progressions every musician should learn, appreciate, and utilize.
The Bottom Line
Drawing from the aforementioned chord progressions, it’s evident that they are an essential framework within the realm of music composition.
With their capability to evoke a myriad of moods and feelings, they are vital in generating a versatile tonal landscape.
While certain progressions like the I-IV-V (1-4-5) or I-V-vi-IV (1-5-6-4) are traditionally more popular in various music genres, other progressions like I-V-IV-iv (1-5-4-2) or I-iii-IV-V (1-3-4-5) offer an alternative soundscape that aids creativity.
Overall, the understanding of these chord progressions and their wise application enables the creation of engaging and diverse musical pieces.
In love with guitars, and gear; expert in all things music! Been writing about guitars for about 5 years and counting. Born in the ’90s. Alma Mater: University of Havana. Always curious, trying to understand the world. #TeamFender




